REST API
Introduction
Jello provides a very powerful and comprehensive RESTful implementation that follows the OData specification. OData (Open Data Protocol) helps you focus on your business logic while building RESTful APIs without having to worry about the different approaches to fetch and interact with the data.
With Jello REST, you get complete support for all CRUD (Create, Retrieve, Update, Delete) operations and can construct complex queries to manipulate the data retrieval structure.
Jello offers a clean, and simple to follow, JSON format. Its protocol schema follows the OData specification.
This document is not intend to cover all OData protocol details.
* For complete reference of the OData protocol, please refer to OData official documentation.
URI Components

The following is an example URI broken down into its component parts:
http://jello-framework.com/jello/data/app.catalog/Category(1)/products?$top=2&$orderby=name
________________________________/___/ _______________________________/____________________/
| | | |
service root URI aspect resource path query options
- Request Aspects
- Resource path
- CRUD operations
- Query options
- Other API options
- Errors and response types
Request Aspects
data
data request aspect is used to perform all CRUD operations and to invoke actions.
Example: /jello/data/demo.inventory/Product

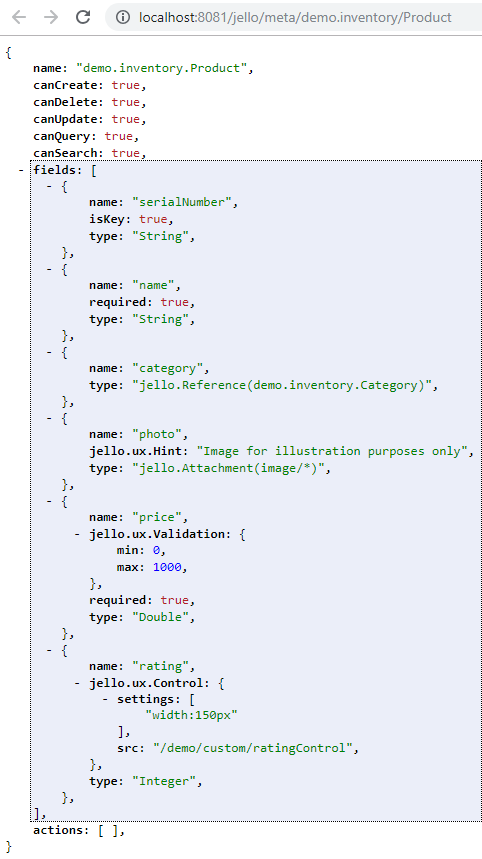
meta
meta request aspect is used to get an entity's metadata.
Example: /jello/meta/demo.inventory/Product
view
Jello offers a unique out-of-the-box data views feature in addition to the OData protocol.
By simply replacing the protocol /jello/data/ prefix with /jello/view/ you will get UI views
so you can test your application and start to interact with the data instantly.
Example: /jello/view/demo.inventory/Product

Resource path
Consider the following Entity definition:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | package app.demo; @View(name="newest", top=10, orderBy="yearModel") public class Car extends JelloEntity { @Expose @KeyElement String licensePlate; @Expose @KeyElement String registeredAtState; @Expose Integer yearModel; @Expose @Association(mappedBy="car") List<Driver> drivers; @Accessible public void beep() {...} } |
You can accesses the entities data by invoking one of the following resource requests:
| Resource request | URI |
|---|---|
| Namespace | .../jello/<aspect>/app.demo |
| Entity - List of records | .../jello/<aspect>/app.demo/Car |
| Entity's records count | .../jello/<aspect>/app.demo/Car/$count |
| Entity's view see @View annotation |
.../jello/<aspect>/app.demo/Car::newest |
| Instance | .../jello/<aspect>/app.demo/Car(1234-CA) |
| Element | .../jello/<aspect>/app.demo/Car(1234-CA)/yearModel |
| Element value | .../jello/<aspect>/app.demo/Car(1234-CA)/yearModel/$value |
| Association element | ../jello/data/app.demo/Car(1234-CA)/drivers[0] |
| Action invocation |
.../jello/<aspect>/app.demo/Car(1234-CA)/beep() |
CRUD operations
Retrieve record:
GET: ../jello/datat/app.demo/Car(1234-CA)
Create record:
POST: ../jello/datat/app.demo/Car
POST body preload: {"licensePlate" : "1234-AB", "registeredAtState" : "CA", "yearModel", 2013}
Update (overwrite) record:
PUT: ../jello/datat/app.demo/Car(1234-AB-CA)
PUT body preload: {"licensePlate" : "1234-AB", "registeredAtState" : "CA", "yearModel", 2000}
Patch (partial update) record:
POST: ../jello/datat/app.demo/Car(1234-AB-CA)
request header: "X-HTTP-Method" = "MERGE"
POST body preload: {"CA", "yearModel", 2000}
Delete record:
DELETE: ../jello/datat/app.demo/Car(1234-AB-CA)
Batch delete:
DELETE: ../jello/datat/app.demo/Car(1234-AB-CA,555-NY,666-NV)
Delete by query:
DELETE: ../jello/datat/app.demo/Car?$filter=yearModel eq 2001
Query options
All Jello request options are passed as URl parameters and prefixed with a '$' sign. You can include other custom parameters in the request URL as long as they do not start with '$'.
Syntax:
/...?$param-1=value1¶m-2=value-2&...¶m-N=value-N
$filter
Specifies a filter to apply to the REST query.
Jello relays on the underlining App Engine implementation to retrieve data from Cloud Datastore. You can query for entities in a way almost reminiscent of an RDBMS in an SQL like syntax. However, for performance reasons, there are some restrictions on the filter expression.
For OData compatibility, both JDOQL and OData operators can be used.
This document is not intended to be a comprehensive explanation of queries and indexes; only what you need to know to use Jello. You should read and understand the GAE Documentation For Queries and Indexes.
| Operator (JDOQL syntax) | Operator (OData equivalent) | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
== |
eq |
Equal to |
< |
lt |
Less than |
<= |
le |
Less than or equal to |
> |
gt |
Greater than |
>= |
ge |
Greater than or equal to |
!= |
ne |
Not equal to |
|| |
OR |
Logical "or" |
&& |
AND |
Logical "and" |
The filter syntax support literals as demonstrated in the following table:
| Type | Literal syntax example |
|---|---|
String |
$filter=category == Electronics |
Numeric (Integer) |
$filter=price < 200 |
Numeric (floating point) |
$filter=price < 200.0 |
Date |
$filter=createdOn < \DATE(milliseconds)\ (coming soon) |
Reference |
$filter=producer == demo.inventory.Category(Bike) |
Examples:
/jello/data/demo.inventory/Product?$filter=price>30.0
/jello/data/demo.inventory/Product?$filter=price>30.0 and price<900
/jello/data/demo.inventory/Product?$filter=name == "Road Bike"
/jello/data/demo.inventory/Product?$filter=name != "Road Bike"
/jello/data/demo.inventory/Product?$filter=category == null
/jello/data/demo.inventory/Product?$filter=category != null
/jello/data/demo.inventory/Product?$filter=category == demo.inventory.Category(Bike)
$search
Free textual search across all entity fields.
By default, Jello will make a best effort to index all the fields for a given entity.
(See @Searchable for more details.)
If $inlinecount is specified, __matchedCount entry will be added to the response showing the number of matched results.
Examples:
/jello/data/demo.inventory/Product?$inlinecount=allpages&$search=Mountain
$orderby
Specifies which field(s) to sort the result-set by. $orderby sorts the records in ascending order by default. To sort the records in a descending order, you can use the DESC keyword.
Syntax:
$orderby=field1[ ASC|DESC][,field2 [ ASC|DESC],...,fieldN [ ASC|DESC]]
Examples:
/jello/data/demo.inventory/Product?$orderby=price
/jello/data/demo.inventory/Product?$orderby=price DESC
/jello/data/demo.inventory/Product?$orderby=category DESC,name ASC
$audit
Use this option to include Audit fields in the response. Audit fields are not included in the REST response by default (see Audit fields for more details).
Example: /jello/data/demo.inventory/Category?$audit=true
$expand
To conserve resources (bandwidth, CPU, DB calls, and so on), Jello will defer sending Reference
and Associations
entries unless the client explicitly asks for them using the $expand option.
Syntax:
$expand=*|field-1[(id)],[ field-2[(id)],...,field-N[(id)]][/*|field-1[(id)],[ field-2[(id)],...,field-N[(id)]]]
The syntax of an $expand query option is a comma-separated list of deferred elements.
Additionally each level can be followed by a forward slash and another list of deferred elements to enable identifying a multi-level relationship.
It is also possible to narrow the expanded expression only to a specific path along the entities hierarchy by specifying an instance ID. This can be very useful when you need to expand an entity's tree to retrieve a specific child. (See also Hierarchy relationship)
Examples:
/jello/data/demo.showbiz/Movie?$expand=*
/jello/data/demo.showbiz/Movie?$expand=cast
/jello/data/demo.showbiz/Movie?$expand=cast(Gone with the Wind)
/jello/data/demo.showbiz/Movie?$expand=*/*
/jello/data/demo.showbiz/Movie?$expand=*/star/photo
/jello/data/demo.showbiz/Movie?$expand=cast,producer/*/photo
$select
By default, the response will include all accessible fields. Use this option to specify which fields to include in the response.
Syntax:
$select=[ONE] field-1[ as alias],[ field-2,...,field-N]
Examples:
/jello/data/demo.inventory/Product?$select=name,price
/jello/data/demo.inventory/Product?$select=name as key,price as value
/jello/data/demo.inventory/Product?$select=ONE name,price
$top
Specify how many records to retrieve.
Example: /jello/data/demo.inventory/Product?$top=2
$skip
Specify the number of results to skip before returning the first one.
Examples:
/jello/data/demo.inventory/Product?$skip=2
/jello/data/demo.inventory/Product?$skip=1&$top=2
$cursor
Query cursors allow an application to retrieve a query's result in convenient batches without incurring the overhead of a query offset.
For any subset query, a __next entry will be added to the result set, specify the URI for retrieving the next batch.
This URI contains the cursor value.
$inlinecount
Use this option to include records and associations count in the response.
__count entry will be added to the response showing the total number of accessible records
(after applying any $filter Query Options).
Syntax:
$inlinecount=allpages|none[/*|association-field_1,...,association-field_N]
Examples:
/jello/data/demo.showbiz/Movie?$inlinecount=none (The default behavior)
/jello/data/demo.showbiz/Movie?$inlinecount=allpages
/jello/data/demo.showbiz/Movie?$inlinecount=allpages/*
/jello/data/demo.showbiz/Movie?$inlinecount=allpages/cast

Other API options
$debugLevel
Set the verbose level. Use this option to receive more details in the error message. Possible values: 1,2,3,4,... where levels of 3 and up are available only for admin users.
Example: /jello/data/demo.inventory/Product(p-1)?$debuglevel=3
The debugLevel is available via the Java API as part of the rest request option object (Request.options.debugLevel)
$asTransaction
Execute any CRUD operation or Action inside a transaction.
* See Transactions for more details
$prettyPrinting
By default, Jello returns JSON responses as a compressed string, omitting all white spaces and line breaks. Use this option to return formatted results.
Usage: /jello/data/demo.inventory/Product?$prettyPrinting=true
Concurrency control and ETags
* See application settings for more details
Removing jello copyrights
* See application settings for more details
Errors and response types
More details coming soon
Was this page helpful? Let us know how we did:
Last updated March 20, 2019.